ANS-313 AMSAT News Service Weekly Bulletins

AMSAT News Service
ANS-313
November 9, 2025
In this edition:
* SpaceX Bandwagon-4 Mission Places CEVROSAT-1 in Orbit with Rideshare Payloads
* CatSat to Open Microwave Linear Transponder Access for Amateur Radio Community
* ARISS to Mark 25 Years of ISS With Special Worldwide SSTV Event in November
* Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications Adds AMSAT Publications
* AI Fix from Earth Restores James Webb Telescope Clarity, No Astronauts Needed
* Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution for November 7, 2025
* ARISS News
* AMSAT Ambassador Activities
* Satellite Shorts From All Over
The AMSAT® News Service bulletins are a free, weekly news and information service of AMSAT, The Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation. ANS publishes news related to Amateur Radio in Space including reports on the activities of a worldwide group of Amateur Radio operators who share an active interest in designing, building, launching and communicating through analog and digital Amateur Radio satellites.
The news feed on https://www.amsat.org publishes news of Amateur Radio in Space as soon as our volunteers can post it.
Please send any amateur satellite news or reports to: ans-editor [at] amsat.org
You can sign up for free e-mail delivery of the AMSAT News Service Bulletins via the ANS List; to join this list see: https://mailman.amsat.org/postorius/lists/ans.amsat.org/
SpaceX Bandwagon-4 Mission Places CEVROSAT-1 in Orbit with Rideshare Payloads
SpaceX launched its Bandwagon-4 rideshare mission on November 2 at 0509 UTC from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, deploying eighteen satellites into a mid-inclination low Earth orbit. The flight is part of SpaceX’s dedicated mid-inclination rideshare program, complementing the Transporter series that serves sun-synchronous orbit customers. All spacecraft were successfully released from the Falcon 9 upper stage approximately seventy-five minutes after liftoff.
The manifest included CEVROSAT-1, an amateur radio satellite built by CEVRO University in the Czech Republic in partnership with Mendel University in Brno and Brno University of Technology. The 48-kilogram microsatellite carries a 9k6 G3RUH GFSK digipeater and AX.25 telemetry on 436.025 MHz, coordinated through the IARU. First signals were received shortly after deployment, with amateur operators reporting telemetry and digipeated packets and uploading frames to the SatNOGS network. The satellite supports student research, hands-on engineering education, and amateur radio experimentation, including an Earth-imaging payload and an optical reflector system for laser technology trials.
The largest spacecraft on the mission was a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging satellite for South Korea’s Project 425 defense reconnaissance program. This continues South Korea’s partnership with SpaceX to deploy a constellation of independent surveillance satellites, following earlier launches on previous Bandwagon missions. The spacecraft is expected to provide high-resolution radar imagery to support national security and intelligence activities.

Commercial space station developer Vast deployed its Haven-Demo spacecraft, a 500-kilogram technology demonstrator designed to validate systems for the upcoming Haven-1 private station. The satellite will test avionics, communications, propulsion, and power systems in orbit. In addition, Starcloud launched Starcloud-1, a technology demonstration spacecraft billed as the first on-orbit artificial-intelligence compute node, featuring an advanced Nvidia processor intended to run large language models in space.
The Bandwagon-4 mission demonstrates the increasing diversity of spacecraft utilizing commercial rideshare launches, spanning defense, scientific, commercial, and amateur radio missions. With CEVROSAT-1 now active on orbit, radio amateurs are encouraged to monitor 436.025 MHz and submit reception reports as commissioning continues.
Read the full article at: https://spacenews.com/spacex-launches-fourth-bandwagon-rideshare-mission/
[ANS thanks Jeff Foust, SpaceNews, and the Libre Space community, for the above information]
CatSat to Open Microwave Linear Transponder Access for Amateur Radio Community
The CatSat team has announced that preparations are underway to open public operation of the spacecraft’s linear transponder, offering the amateur-radio community a new microwave-band satellite resource. CatSat, a 6U CubeSat developed and flown by students, faculty, and staff at the University of Arizona in partnership with FreeFall Aerospace and Rincon Research, has been on orbit since July 2024 and is now entering the phase of its mission focused on community engagement and technology demonstration.
CatSat was launched aboard a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base as part of NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative. Measuring roughly the size of a family-size cereal box, the spacecraft carries a suite of experimental payloads, including a novel inflatable antenna capable of enabling large-aperture communications from a small satellite platform. In addition to ionospheric monitoring via high-frequency (HF) radio measurements and imaging of the Earth, CatSat includes a linear transponder for amateur radio, extending the University of Arizona’s long legacy in space science down to hands-on student involvement.
The satellite orbits Earth in a nearly sun-synchronous polar orbit, circling the globe approximately every 90 minutes. As part of its student-driven mission, CatSat is demonstrating how cutting-edge antenna systems and commercial-off-the-shelf radio hardware can support meaningful research and amateur communications from a compact form factor. The mission is funded by the University of Arizona Office of the Vice President for Research and the Arizona Space Institute, with additional support from industry partners.
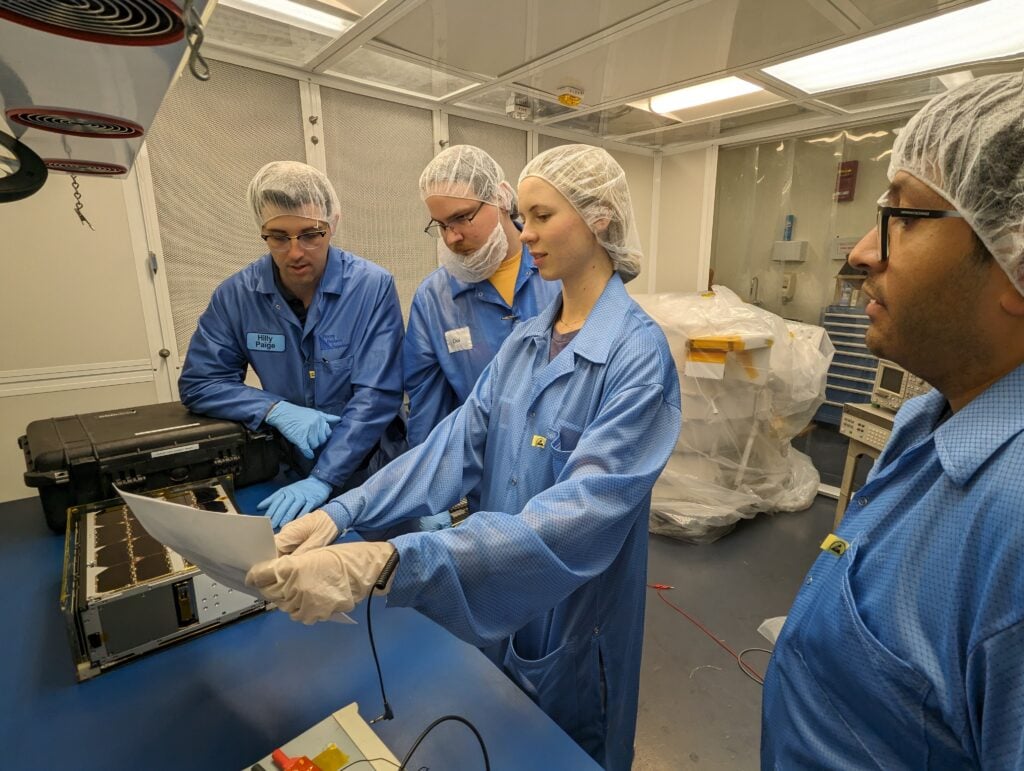

Early on-orbit demonstrations used a 1-meter C-band uplink dish and a 6.1-meter X-band downlink dish to confirm transponder functionality, successfully relaying Morse code. The CatSat team is now constructing a more accessible ground station using 1-meter-class commercial antennas to show that amateur access is practical with reasonably sized equipment. Operators will be able to monitor schedule updates — informally known as the “five and dime” plan — through the CatSat mission website.
Commissioning passes targeting the CatSat ground stations in Tucson took place on October 29 and November 2, with one final activation scheduled for November 9 at approximately 7:50 PM MST (UTC-7) — just hours after this bulletin’s publication. As testing continues, dates may shift as the team evaluates performance and power-budget constraints. Operators can follow activation plans and future opportunities at https://catsat.arizona.edu.
Read the full announcement at: https://catsat.arizona.edu/news/catsat-team-preparing-public-linear-transponder-operations
[ANS thanks the CatSat Team and the University of Arizona for the above information]
Only 7 Weeks Left to Get Your Coin!
Celebrate the 40th Anniversary of Amateur Radio on Human Spaceflight
Help Support GOLF and FoxPlus.
Annual memberships start at only $120
Join the AMSAT President’s Club today and help
Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
https://www.amsat.org/join-the-amsat-presidents-club/
ARISS to Mark 25 Years of ISS With Special Worldwide SSTV Event in November
Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS) will commemorate the 25th anniversary of continuous human presence aboard the International Space Station with a special worldwide Slow-Scan Television (SSTV) event in mid-November. The ISS has been continuously inhabited since November 2, 2000, marking a major milestone in human spaceflight and international cooperation. ARISS, the first educational payload on the station, continues to play a key role in inspiring students, supporting STEM engagement, and connecting the global amateur radio community with astronauts in orbit.
The Series 30 SSTV event, titled “ISS at 25 and Scouts!” will feature 12 SSTV images celebrating the station’s 25-year milestone and Scouting. Transmissions are scheduled to begin Wednesday, November 12 around 1730 UTC and continue through Thursday, November 20 (time TBD). Downlink will occur on 145.800 MHz FM using the PD120 mode, following the standard ARISS pattern of approximately two minutes of transmission followed by two minutes off. A planned pause in images will occur to support an ARISS school contact with Azerbaijan on November 16 at 1450 UTC.
Radio amateurs and listeners worldwide are encouraged to participate, as ISS SSTV events are accessible to stations with a broad range of equipment. Many operators successfully receive images using only a handheld VHF radio and a phone-based decoding app, while more advanced satellite stations can produce particularly clean results. SSTV events continue to be a popular entry point for newcomers interested in amateur space communication.

In keeping with past ARISS activities, operators may also request a traditional ARISS QSL card to confirm SSTV reception. QSL requests must be mailed to the appropriate regional bureau with a self-addressed stamped envelope or sufficient return postage. Details and mailing addresses for each world region are available at https://www.ariss.org/qsl-cards.html, and operators should include date, time, frequency, and mode with their report.
Additional updates and operating details will be posted on www.ariss.org and ARISS social media channels as the event approaches. AMSAT congratulates ARISS and the ISS program on 25 years of continuous human presence aboard the station and encourages radio amateurs everywhere to join in this special commemorative SSTV celebration honoring the ISS legacy and the role of amateur radio in space education.
[ANS thanks Amateur Radio on the International Space Station (ARISS) for the above information]
Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications Adds AMSAT Publications
The Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications recently added publications provided by AMSAT from 1969-2013 to the Internet Archive. These include the vast majority of issues of the AMSAT Newsletter, AMSAT Satellite Report, AMSAT’s ORBIT magazine, and The AMSAT Journal for that time period.
The Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications is a library of materials and collections related to amateur radio and early communications. The DLARC is funded by a significant grant from Amateur Radio Digital Communications, a private foundation, to create a digital library that documents, preserves, and provides open access to the history of this community.
The Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications can be accessed at https://archive.org/details/dlarc
AMSAT publications can be found at https://archive.org/search?query=creator%3A%22AMSAT%22
Issues of The AMSAT Journal from 2014 to the present can be accessed by AMSAT members at https://launch.amsat.org/The_AMSAT_Journal
[ANS thanks the Digital Library of Amateur Radio and Communications for the above information]
AI Fix from Earth Restores James Webb Telescope Clarity, No Astronauts Needed
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has received a remarkable upgrade — not from astronauts or hardware, but from artificial intelligence. Researchers at the University of Sydney developed a software-based solution that corrected subtle image blurring in one of JWST’s most sensitive instruments, restoring the telescope’s precision without the need for any on-orbit servicing mission.
The issue affected JWST’s Aperture Masking Interferometer (AMI), a specialized instrument designed to resolve extremely fine features when observing stars and exoplanets. Soon after operations began, scientists noticed faint distortions caused by tiny electronic effects within the infrared detector. Rather than planning a complex repair mission, similar to how astronauts serviced the Hubble Space Telescope decades ago, the team pursued a software-only approach.
Two PhD researchers, Louis Desdoigts and Max Charles, created a new calibration system called AMIGO that uses artificial intelligence to model the behavior of JWST’s detector in space. By correcting a phenomenon known as the “brighter-fatter effect,” where electrical charge slightly spreads between pixels, their software restored AMI’s ability to produce extremely sharp, high-contrast images from millions of miles away.

The effort highlights a growing era where software and artificial intelligence can enhance or even “repair” spacecraft from the ground. “Instead of sending astronauts to bolt on new parts, they managed to fix things with code,” said Professor Peter Tuthill of the University of Sydney, whose group originally contributed the AMI instrument design for JWST. The achievement underscores both the telescope’s flexibility and Australia’s strong role in cutting-edge astronomical instrumentation.
The research has now been publicly released and peer-review is underway. The software tools are being prepared for use by the broader JWST science community, ensuring the telescope continues delivering unmatched views of the universe — all thanks to a clever fix developed on Earth, with no spacewalks or hardware intervention required.
Read the full article at: https://scitechdaily.com/how-ai-saved-nasas-10-billion-webb-telescope-from-blurry-vision/
ANS thanks University of Sydney and SciTechDaily for the above information]
AMSAT Remove Before Flight Key Tags Now Available
Yes, These are the Real Thing!
Your $20 Donation Goes to Help Fly a Fox-Plus Satellite
Includes First Class Postage (Sorry – U.S. Addresses Only)
Order Today at https://www.amsat.org/product/amsat-remove-before-flight-keychain
Changes to AMSAT TLE Distribution for November 7, 2025
Two Line Elements or TLEs, often referred to as Keplerian elements or keps in the amateur community, are the inputs to the SGP4 standard mathematical model of spacecraft orbits used by most amateur tracking programs. Weekly updates are completely adequate for most amateur satellites. TLE bulletin files are updated daily in the first hour of the UTC day. New bulletin files will be posted immediately after reliable elements become available for new amateur satellites. More information may be found at https://www.amsat.org/keplerian-elements-resources/.
This week there are no additions or deletions to the AMSAT TLE distribution.
[ANS thanks Joe Fitzgerald, KM1P, AMSAT Orbital Elements Manager, for the above information.]
ARISS News
Amateurs and others around the world may listen in on contacts between amateurs operating in schools and allowing students to interact with astronauts and cosmonauts aboard the International Space Station. The downlink frequency on which to listen is 145.800 MHz worldwide.
Scheduled Contacts
+ Recently Completed
Petőfi Sándor Evangélikus Gimnázium, Kollégium és Általános Iskola, Mezőberény, Hungary, Telebridge via K6DUE
The ISS callsign was NA1SS
The scheduled crewmember was Jonathan (Jonny) Kim KJ5HKP
Contact was successful: Fri 2025-11-07 08:13:22 UTC
Watch the Livestream at https://www.facebook.com/share/16x7e1jvTv/ and https://www.facebook.com/mpseg/live_videos/
+ Upcoming Contacts
Colegio Del Faro, Benavídez, Tigre, Argentina, direct via LU4BB
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be NA1SS
The scheduled crewmember is Mike Fincke KE5AIT
The ARISS mentor is VE3TBD
Contact is go for: Tue 2025-11-11 18:18 UTC
SPACE Academy of Azercosmos, Baku, Azerbaijan, direct via 4K4AZE
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be OR4ISS
The scheduled crewmember is Mike Fincke KE5AIT
The ARISS mentor is SP3QFE
Contact is go for: Sun 2025-11-16 14:53 UTC
Russian school TBD, direct via TBD
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be RSØISS
The scheduled crewmember is Oleg Platonov
The ARISS mentor is RV3DR
Contact is go for Tue 2025-11-18 10:10 UTC
Russian school TBD, direct via TBD
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be RSØISS
The scheduled crewmember is Oleg Platonov
The ARISS mentor is RV3DR
Contact is go for Thu 2025-11-20 14:50 UTC
Many times a school may make a last-minute decision to do a Livestream or run into a last-minute glitch requiring a change of the URL but we at ARISS may not get the URL in time for publication. You can always check https://live.ariss.org/ to see if a school is Livestreaming.
As always, if there is an EVA, a docking, or an undocking; the ARISS radios are turned off as part of the safety protocol.
The crossband repeater continues to be active (145.990 MHz up {PL 67} & 437.800 MHz down), If any crewmember is so inclined, all they have to do is pick up the microphone, raise the volume up, and talk on the crossband repeater. So give a listen, you just never know.
Packet operations continue to be active (145.825 MHz up & down). HamTV is configured (2395.00 MHz).
Note, all times are approximate. It is recommended that you do your own orbital prediction or start listening about 10 minutes before the listed time.
The latest information on the operation mode can be found at https://www.ariss.org/current-status-of-iss-stations.html
The latest list of frequencies in use can be found at https://www.ariss.org/contact-the-iss.html
[ANS thanks Charlie Sufana, AJ9N, one of the ARISS operation team mentors for the above information.]
AMSAT Ambassador Activities
AMSAT Ambassadors provide presentations, demonstrate communicating through amateur satellites, and host information tables at club meetings, hamfests, conventions, maker faires, and other events.
AMSAT Ambassador Clint Bradford, K6LCS, says,
“Think a 75-minute presentation on “working the easy satellites” would be appropriate for your club or event? Let me know by emailing me at k6lcsclint (at) gmail (dot) com or calling me at 909-999-SATS (7287)!”
Clint has NEVER given the exact same show twice: EACH of the 150+ presentations so far has been customized/tailored to their audiences.
Scheduled Events
None currently scheduled.
For more information go to: https://www.amsat.org/ambassador/
[ANS thanks Bo Lowrey, W4FCL, Director – AMSAT Ambassador Program, for the above information.]
Want to fly the colors on your own grid expedition?
Get an AMSAT car flag and other neat stuff from our Zazzle store!

25% of the purchase price of each product goes towards Keeping Amateur Radio in Space
Satellite Shorts from All Over
+ AMSAT proudly recognizes two new operators who have earned the prestigious GridMaster Award. David Fisher, KG0D, achieved GridMaster Award #77 on October 19, 2025, followed by Gene Eighmy, KJ4M, who earned Award #78 on October 22, 2025. The GridMaster Award honors amateur satellite operators who successfully confirm contacts from all 488 Maidenhead grid squares across the continental United States — a challenge requiring exceptional operating skill, patience, and commitment. These accomplishments reflect not only the determination of the recipients but also the strong support and activity of the portable operators who make rare grid contacts possible. With only a small number of amateurs having reached this milestone, each new award represents a significant achievement within the satellite community. Congratulations to David and Gene on reaching this elite level of satellite operating excellence. (ANS thanks Bruce Paige, KK5DO, AMSAT Director of Contests & Awards, for the above information)
+ Elon Musk’s Starlink has made satellite internet service free to residents in Jamaica and the Bahamas following widespread communications outages caused by Hurricane Melissa. Starlink says the temporary measure is intended to support emergency response and recovery efforts as infrastructure repairs continue. Although service fees are waived through the end of November, new users would still need to purchase a Starlink terminal if they don’t already have one. The company also enabled direct-to-cell service in Jamaica via Liberty Caribbean, allowing compatible phones to connect directly to Starlink satellites during terrestrial network disruptions. Starlink’s low-Earth-orbit constellation provides lower latency than traditional geostationary satellite internet, making it useful in disaster environments where real-time communication is critical, especially for first responders and emergency coordinators. SpaceX has offered similar emergency access before, including after major flooding in Texas and during Hurricanes Helene and Milton in 2024, reflecting an ongoing pattern of deploying satellite support during major disasters. (ANS thanks USA Today for the above information)
+ A historic 26-meter radio dish in Rosman, North Carolina—now part of the Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute (PARI)—once served NASA’s Space Tracking and Data Acquisition network and later supported U.S. intelligence operations during the Cold War. Established in 1962, the site tracked early NASA satellites, supported Apollo recovery communications, and later hosted NSA signals-intelligence missions before being decommissioned in the 1990s. PARI’s nonprofit owners have since preserved the facility as an education and research campus, hosting camps, astronomy programs, and university instruments while maintaining operational deep-space-capable antennas. The institute recently listed portions of its 192-acre campus for sale or lease, seeking a partner who will continue its STEM outreach mission rather than convert the property to private development. PARI maintains real tracking capability, recently receiving signals from Intuitive Machines’ IM-1 lunar lander and preparing to listen for NASA’s Artemis II Orion spacecraft regardless of official involvement. Leaders stress that PARI is not shutting down, and they aim to secure support from the growing commercial space sector to keep the iconic “26 West” dish operating as a public educational and scientific asset. (ANS thanks Space.com for the above information)
+ Prusa Research has introduced Prusament PC Space Grade Black, a 3D-printing filament engineered for aerospace projects and developed in cooperation with TRL Space. The material meets European Space Agency (ESA) outgassing standards and provides electrostatic-dissipative protection, making it suitable for satellite components and electronics housings used in space environments. Mechanical testing shows it exceeds key strength and temperature requirements for CubeSat structures, demonstrating potential for lightweight printed parts on future missions. Unlike traditional space-qualified plastics that require expensive industrial printers, this filament can be printed on standard Prusa desktop systems with a hardened nozzle. That makes high-reliability parts and space-hardware prototyping significantly more affordable and accessible to universities, labs, and advanced hobbyists. With strong performance in vacuum, thermal, and ESD conditions, the material opens exciting possibilities for low-cost satellite development and electronics protection on Earth and beyond. (ANS thanks Prusa Research for the above information)
Join AMSAT today at https://launch.amsat.org/
In addition to regular membership, AMSAT offers membership to:
- Societies (a recognized group, clubs or organization).
- Primary and secondary school students are eligible for membership at one-half the standard yearly rate.
- Post-secondary school students enrolled in at least half-time status shall be eligible for the student rate for a maximum of 6 post-secondary years in this status.
- Memberships are available for annual and lifetime terms.
Contact info [at] amsat.org for additional membership information.
73 and remember to help Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
This week’s ANS Editor,
Mitch Ahrenstorff, ADØHJ
mahrenstorff [at] amsat.org
ANS is a service of AMSAT, the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation, 712 H Street NE, Suite 1653, Washington, DC 20002
AMSAT is a registered trademark of the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation.