ANS-004 AMSAT News Service Weekly Bulletins

AMSAT News Service
ANS-004
January 4, 2026
In this edition:
* AMSAT Membership Now Includes “Getting Started with Amateur Satellites” Guide
* Soyuz Rideshare Launch Deploys Several New Amateur Radio Satellites in Orbit
* HDMI Converter Installed on ISS HamTV System, Expanding Video Capabilities
* CubeSat Developers Workshop 2026 Opens Call for Abstract Submissions
* GridMasterMap Satellite Top 100 Rovers January 2026 Rankings
* Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution for January 2, 2026
* ARISS News
* AMSAT Ambassador Activities
* Satellite Shorts From All Over
The AMSAT® News Service bulletins are a free, weekly news and information service of AMSAT, The Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation. ANS publishes news related to Amateur Radio in Space including reports on the activities of a worldwide group of Amateur Radio operators who share an active interest in designing, building, launching and communicating through analog and digital Amateur Radio satellites.
The news feed on https://www.amsat.org publishes news of Amateur Radio in Space as soon as our volunteers can post it.
Please send any amateur satellite news or reports to: ans-editor [at] amsat.org
You can sign up for free e-mail delivery of the AMSAT News Service Bulletins via the ANS List; to join this list see: https://mailman.amsat.org/postorius/lists/ans.amsat.org/
AMSAT Membership Now Includes “Getting Started with Amateur Satellites” Guide
AMSAT is offering a limited-time promotion for new and renewing members that includes a free digital copy of Getting Started with Amateur Satellites. The promotion is being offered as AMSAT begins the 2026 membership year.
Anyone who joins or renews their AMSAT membership during the promotional period will receive a download link for the latest edition of Getting Started with Amateur Satellites in their membership confirmation email. The guide is designed to help radio amateurs understand the fundamentals of satellite operation and serves as a practical reference for both newcomers and operators returning to the hobby. Additional information about AMSAT membership is available at https://launch.amsat.org.
In addition to this limited-time promotion, AMSAT membership includes a subscription to The AMSAT Journal, access to archived issues, discounts on selected items in the AMSAT online store, and opportunities to participate in AMSAT elections, committees, awards programs, and other AMSAT activities and programs. Members may also access archived proceedings from past AMSAT Space Symposiums through the AMSAT member portal.
Beyond these tangible benefits, AMSAT membership supports the development, launch, and operation of amateur radio satellites, along with education and outreach efforts. Joining AMSAT is not just about individual benefits — it is about being part of the community that builds and operates amateur satellites for radio amateurs worldwide. As AMSAT looks ahead to 2026, the promotion helps launch another year of growth and opportunity for amateur radio in space.
[ANS thanks Drew Glasbrenner, KO4MA, AMSAT President and BoD member, for the above information]
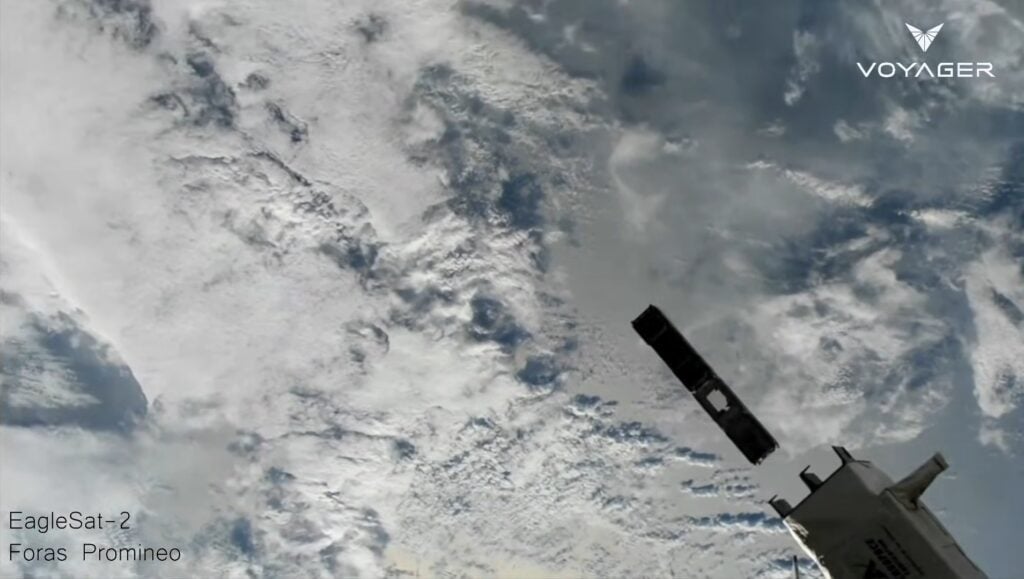
Soyuz Rideshare Launch Deploys Several New Amateur Radio Satellites in Orbit
A Soyuz-2.1b launch vehicle with a Fregat upper stage launched successfully on December 28 at 13:18 UTC (8:18 a.m. EST), deploying a total of 52 satellites into orbit. The mission was operated by Roscosmos and lifted off from the Vostochny Cosmodrome in eastern Siberia. The primary payloads were two Aist-2T Earth-observation satellites.
Among the secondary payloads were at least eight satellites using amateur radio frequencies, including several that received coordination through the International Amateur Radio Union. Initial on-orbit checkout and commissioning activities are underway, with beacon reports and operational activity continuing to be reported.
QMR-KWT-2 (Moon of Kuwait) is a 1U CubeSat carrying an amateur radio mission led by Oleg Razin, R3AOR, in cooperation with the Moscow Technical University of Communication and Informatics. The satellite features an FM amateur radio transponder intended to encourage participation by students and new operators, along with a miniature camera capable of transmitting SSTV images. The mission operates under IARU coordination, with a downlink on 436.950 MHz and a transponder uplink on 145.920 MHz.
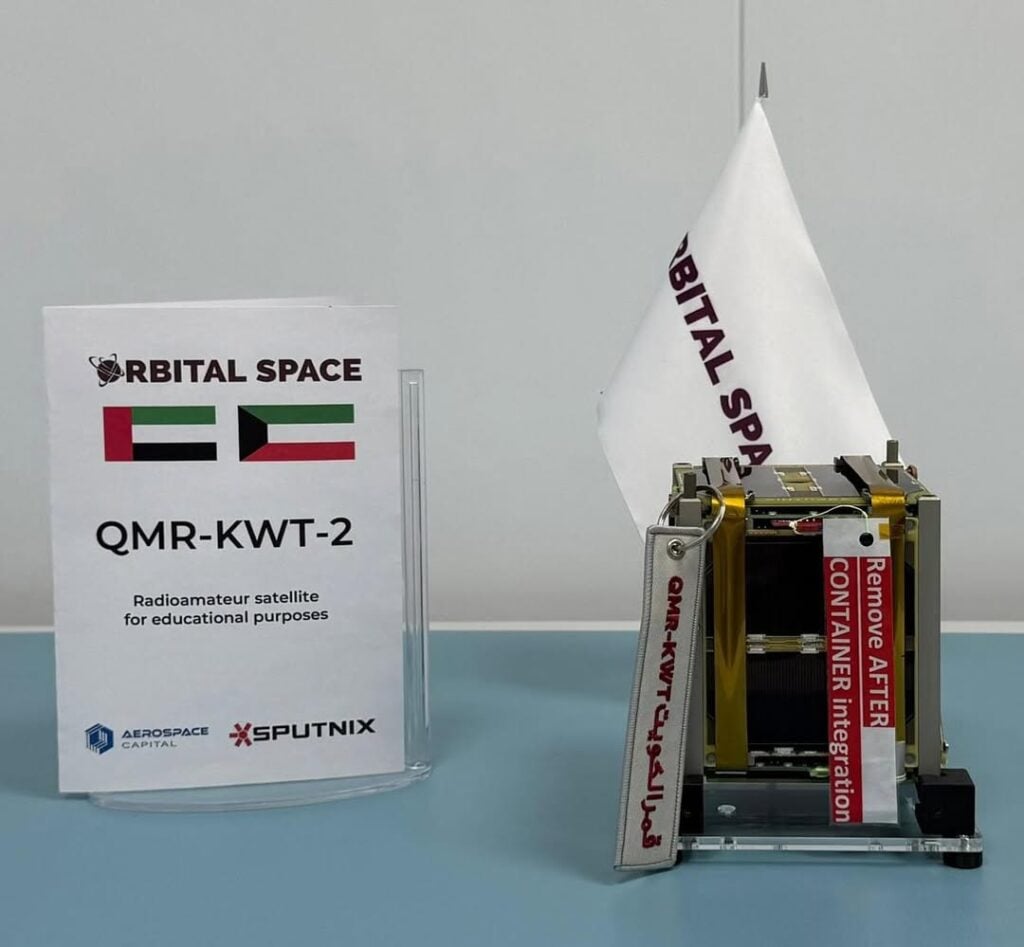

Lobachevsky (RS83S) is a 16U CubeSat developed by the National Research State University of Nizhny Novgorod as part of Russia’s Space-π educational program. The spacecraft carries an amateur radio digital repeater supporting message exchange between radio amateurs worldwide, along with imaging payloads transmitting SSDV and SSTV pictures. IARU-coordinated frequencies include a repeater uplink on 435.500 MHz, repeater downlink on 145.910 MHz, a telemetry and image downlink on 436.320 MHz, and an experimental X-band downlink on 10.470 GHz.
SAKHACUBE-CHOLBON (RS-18S) is a 1U CubeSat developed by the Sakha Science Academy as the first satellite of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). The spacecraft uses a single UHF amateur radio transceiver for telemetry, command, and educational payload data, including digital transmissions and SSTV images. The satellite operates with IARU coordination, including a downlink on 437.350 MHz.
Several additional satellites on the mission are reported to use amateur radio frequencies without IARU coordination, including Polytech Universe-6, Scorpion, Luca-1, and Galapagos-UTE. In addition to the amateur-frequency spacecraft, the mission also deployed three Iranian Earth-observation satellites — Paya, Zafar-2, and Kowsar — intended for monitoring agriculture, mapping natural resources, and studying environmental conditions.
Follow ongoing tracking, decoding activity, and discussion of this launch in the LibreSpace community at: https://community.libre.space/t/soyuz-2-1b-fregat-vostochny-launch-2025-12-28-1305-utc/14152/21
[ANS thanks AMSAT-Francophone, the IARU, and the LibreSpace community for the above information]
HDMI Converter Installed on ISS HamTV System, Expanding Video Capabilities
Amateur Television operations aboard the International Space Station received a significant upgrade on December 22, when an HDMI converter was installed on the ARISS HamTV system. The new hardware expands video capabilities for HamTV and supports the use of a broader range of onboard cameras during future educational contacts. The installation was performed during scheduled maintenance activities by NASA astronaut Chris Williams, KJ5GEW. ARISS reported that the HDMI converter can generate a video test signal when the system is in standby mode, providing a clear visual indication of system readiness and video-path functionality.
The December upgrade builds on HamTV’s return to operation earlier in the year. The HamTV unit was installed aboard the ISS on July 29 by astronaut Jonny Kim, KJ5HKP, after several years offline for repairs. Following installation, ARISS confirmed acquisition of signal reports from amateur stations as the system began transmitting a carrier on 2395 MHz, with continued testing through August confirming stable carrier operation.
Those efforts led to successful video use during an educational contact on October 18 with scouts in the United Kingdom. During that event, Jonny Kim, KJ5HKP, answered student questions while appearing live on station via HamTV. Pre-contact testing included tone and color-bar transmissions, followed by a successful live video downlink from the ISS.
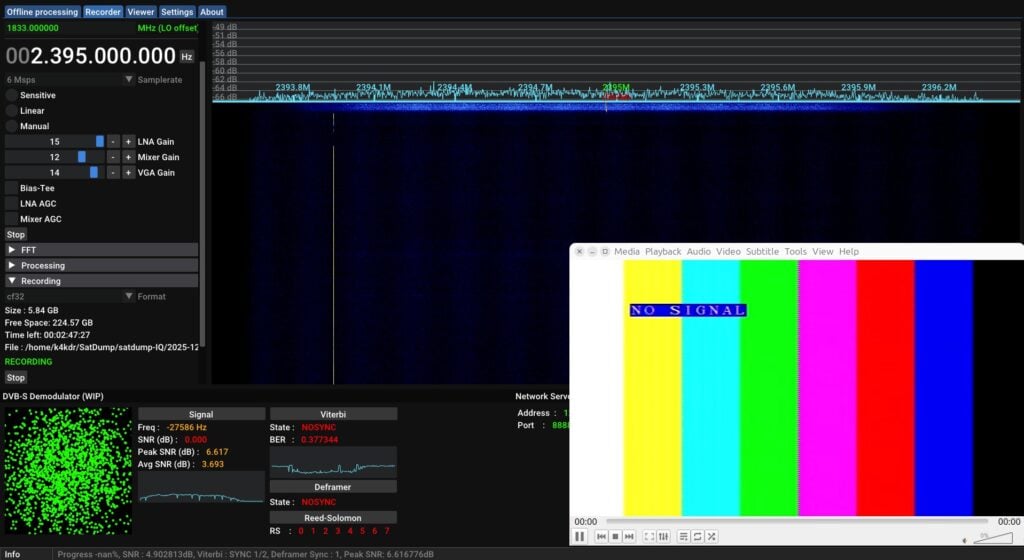
In the days following the December 22 maintenance activity, amateur observers again reported reception of color-bar test signals, confirming proper operation of the updated video chain. On December 23, amateur operator Scott Chapman, K4KDR, reported successful reception of HamTV test video during an ISS pass over North America, documenting decoding of a video test pattern using a one-meter S-band dish.
HamTV uses DVB-S digital amateur television transmitted on 2395 MHz, and reception typically requires a 2.4-GHz-capable antenna, a low-noise amplifier, and a compatible DVB-S receiver or software-defined radio. With the HDMI converter installed and testing completed, ARISS has indicated that further HamTV activity is expected during educational contacts in 2026.
For those interested in receiving HamTV, Scott Chapman, K4KDR, has published a community guide describing one method of decoding and recording HamTV test video using SatDump and VLC Media Player: https://www.qsl.net/k/k4kdr/how-to/HamTV_SatDump_VLC.pdf. Additional technical background, reception reports, and ground-station information are maintained by the British Amateur Television Club (BATC): https://wiki.batc.org.uk/HAMTV_from_the_ISS.
[ANS thanks ARISS, the British Amateur Television Club, and Scott Chapman, K4KDR for the above information]
CubeSat Developers Workshop 2026 Opens Call for Abstract Submissions
The CubeSat Developers Workshop (CDW) team has opened the call for abstracts for the 2026 workshop, inviting members of the CubeSat and small-satellite community to submit presentations covering mission concepts, technical developments, and operational results.
The CubeSat Developers Workshop is an annual three-day global small-satellite conference hosted at California Polytechnic State University in San Luis Obispo, California. The event brings together students, researchers, educators, and industry professionals from around the world to share experience and lessons learned across the CubeSat mission lifecycle. In recent years, the workshop has attracted more than 600 participants representing over 50 countries.
The 2026 workshop will include both oral presentations and poster sessions. Poster sessions provide an interactive forum well suited to early-stage mission concepts, subsystem development, and student projects, while oral presentations focus on more mature missions, flight results, and in-depth technical analyses.
Abstracts are welcomed on topics spanning the full CubeSat mission lifecycle, including mission design, hardware and software development, integration and testing, operations, and on-orbit performance. Submissions that emphasize lessons learned, innovative approaches, or practical operational experience are particularly encouraged.
The CubeSat Developers Workshop 2026 will take place April 14–16, 2026, in San Luis Obispo, California. Abstract submissions must be received no later than 11:59 p.m. Pacific Time on Monday, January 5, 2026. Participant registration is now open, with early-bird pricing available through February 1, 2026. Professional early-bird registration begins at $200 for a one-day pass or $500 for a three-day pass, while student pricing starts at $125 for one day or $225 for three days.
Additional information on abstract submission, registration, sponsorship, and exhibitor opportunities is available on the workshop website: https://www.cubesatdw.org.
[ANS thanks the CubeSat Developers Workshop for the above information]
GridMasterMap Satellite Top 100 Rovers January 2026 Rankings
The January 2026 rankings for the Top 100 Rovers (Mixed LEO/MEO/GEO) in satellite operations, as determined by @GridMasterMap on Twitter, has been released. The ranking is determined by the number of grids and DXCC entities activated, taking into account only those grids where a minimum number of QSOs logged on the gridmaster.fr website have been validated by a third party. Grid numbers do not directly reflect the exact number of activations. Satellite operators are encouraged to upload their LoTW satellite contacts to https://gridmaster.fr in order to provide more accurate data.
Updated: 2026-01-01
| 1 | ND9M | 26 | KX9X | 51 | WD5GRW | 76 | N8RO |
| 2 | NJ7H | 27 | KG5CCI | 52 | KE0PBR | 77 | SP5XSD |
| 3 | UT1FG | 28 | DJ8MS | 53 | XE3DX | 78 | N6UTC |
| 4 | JA9KRO | 29 | N5BO | 54 | W7WGC | 79 | N4UFO |
| 5 | N5UC | 30 | ON4AUC | 55 | PR8KW | 80 | VE7PTN |
| 6 | F5VMJ | 31 | K8BL | 56 | JK2XXK | 81 | BA8AFK |
| 7 | DL6AP | 32 | KE4AL | 57 | LU4JVE | 82 | PT2AP |
| 8 | DP0POL | 33 | KB5FHK | 58 | EB1AO | 83 | VE1VOX |
| 9 | WI7P | 34 | AC0RA | 59 | XE1ET | 84 | AA8CH |
| 10 | K5ZM | 35 | PA3GAN | 60 | EA4NF | 85 | KB2YSI |
| 11 | OE3SEU | 36 | KI0KB | 61 | N6DNM | 86 | KI7UXT |
| 12 | WY7AA | 37 | JO2ASQ | 62 | W8LR | 87 | AF5CC |
| 13 | LU5ILA | 38 | F4BKV | 63 | W1AW | 88 | KJ7NDY |
| 14 | N6UA | 39 | KI7UNJ | 64 | KI7QEK | 89 | BI1MHK |
| 15 | HA3FOK | 40 | VA3VGR | 65 | SM3NRY | 90 | PT9BM |
| 16 | W5PFG | 41 | VE3HLS | 66 | KE9AJ | 91 | FG8OJ |
| 17 | AK8CW | 42 | BG7QIW | 67 | F4DXV | 92 | BG5CZD |
| 18 | N9IP | 43 | LA9XGA | 68 | VE1CWJ | 93 | YU0W |
| 19 | AD0DX | 44 | HJ5LVR | 69 | AA5PK | 94 | PU4CEB |
| 20 | AD0HJ | 45 | VK5DG | 70 | AD7DB | 95 | W8MTB |
| 21 | N4AKV | 46 | N7AGF | 71 | KM4LAO | 96 | N4DCW |
| 22 | DL2GRC | 47 | DF2ET | 72 | M1DDD | 97 | WA9JBQ |
| 23 | ND0C | 48 | K7TAB | 73 | HB9GWJ | 98 | PS8BR |
| 24 | WD9EWK | 49 | JL3RNZ | 74 | VA7LM | 99 | VE3GOP |
| 25 | BA1PK | 50 | KE0WPA | 75 | DL4EA | 100 | JM1CAX |
[ANS thanks @GridMasterMap for the above information]
AMSAT Remove Before Flight Key Tags Now Available
Yes, These are the Real Thing!
Your $20 Donation Goes to Help Fly a Fox-Plus Satellite
Includes First Class Postage (Sorry – U.S. Addresses Only)
Order Today at https://www.amsat.org/product/amsat-remove-before-flight-keychain
Changes to AMSAT TLE Distribution for January 2, 2026
Two Line Elements or TLEs, often referred to as Keplerian elements or keps in the amateur community, are the inputs to the SGP4 standard mathematical model of spacecraft orbits used by most amateur tracking programs. Weekly updates are completely adequate for most amateur satellites. TLE bulletin files are updated daily in the first hour of the UTC day. New bulletin files will be posted immediately after reliable elements become available for new amateur satellites. More information may be found at https://www.amsat.org/keplerian-elements-resources/.
This week there are no additions or deletions to the AMSAT TLE distribution.
[ANS thanks Joe Fitzgerald, KM1P, AMSAT Orbital Elements Manager, for the above information]
ARISS News
Amateurs and others around the world may listen in on contacts between amateurs operating in schools and allowing students to interact with astronauts and cosmonauts aboard the International Space Station. The downlink frequency on which to listen is 145.800 MHz worldwide.
Scheduled Contacts
+ Recently Completed
No International Space Station school contacts were completed during this reporting period, as many schools were closed for the holiday break.
+ Upcoming Contacts
No upcoming school contacts are currently scheduled; scheduling will resume once schools return from the holidays.
Many times a school may make a last-minute decision to do a Livestream or run into a last-minute glitch requiring a change of the URL but we at ARISS may not get the URL in time for publication. You can always check https://live.ariss.org/ to see if a school is Livestreaming.
As always, if there is an EVA, a docking, or an undocking; the ARISS radios are turned off as part of the safety protocol.
The crossband repeater remains configured in the Columbus Module (145.990 MHz up {PL 67} & 437.800 MHz down). If a crewmember decides to pick up the microphone and turn up the volume, you may hear them on the air—so keep listening, as you never know when activity might occur.
The service module IORS is not currently in APRS configuration and is being used only for voice contacts at this time. HamTV in the Columbus Module is configured for scheduled digital amateur television operations on 2395.00 MHz.
Note, all times are approximate. It is recommended that you do your own orbital prediction or start listening about 10 minutes before the listed time.
The latest information on the operation mode can be found at https://www.ariss.org/current-status-of-iss-stations.html
The latest list of frequencies in use can be found at https://www.ariss.org/contact-the-iss.html
[ANS thanks Charlie Sufana, AJ9N, one of the ARISS operation team mentors for the above information]
AMSAT Ambassador Activities
AMSAT Ambassadors provide presentations, demonstrate communicating through amateur satellites, and host information tables at club meetings, hamfests, conventions, maker faires, and other events.
AMSAT Ambassador Clint Bradford, K6LCS, says,
“Think a 75-minute presentation on “working the easy satellites” would be appropriate for your club or event? Let me know by emailing me at k6lcsclint (at) gmail (dot) com or calling me at 909-999-SATS (7287)!”
Clint has NEVER given the exact same show twice: EACH of the 150+ presentations so far has been customized/tailored to their audiences.
Scheduled Events
None currently scheduled.
For more information go to: https://www.amsat.org/ambassador/
[ANS thanks Bo Lowrey, W4FCL, Director – AMSAT Ambassador Program, for the above information]
Want to fly the colors on your own grid expedition?
Get an AMSAT car flag and other neat stuff from our Zazzle store!

25% of the purchase price of each product goes towards Keeping Amateur Radio in Space
Satellite Shorts from All Over
+ South Korean startup Innospace failed in its first orbital launch attempt on December 22, when its Hanbit-Nano rocket lifted off from the Alcântara Space Center in Brazil. The launch marked the first-ever orbital launch attempt by a South Korean commercial company. Hanbit-Nano is a two-stage launch vehicle designed to place small satellites into low Earth orbit from equatorial launch sites. The rocket experienced an anomaly and crashed back to Earth about one minute after liftoff, according to tracking reports. Hanbit-Nano was carrying multiple small satellites on the SPACEWARD mission, including the amateur radio CubeSat Solara S2. The mission also represented a milestone for international cooperation, with Brazil hosting the inaugural launch attempt of the South Korean-developed rocket. Innospace did not immediately disclose the cause of the failure and ended its webcast shortly after the incident. The company has said it will analyze the failure as it continues development of its launch vehicle family. (ANS thanks Space.com for the above information)
+ AST SpaceMobile launched BlueBird 6, the first of its next-generation satellites, on December 23 aboard India’s LVM3 rocket operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation from the Satish Dhawan Space Center. AST SpaceMobile says BlueBird 6 is its largest satellite to date, featuring a deployable antenna substantially larger than those flown on its earlier spacecraft. BlueBird 6 is designed to support the company’s planned space-based cellular broadband network that would connect directly to standard mobile phones without additional hardware. The launch marks the beginning of a new satellite series, with the company planning to deploy dozens more spacecraft in 2026. AST SpaceMobile previously demonstrated its technology using the BlueWalker 3 prototype, including a successful 5G call to an unmodified smartphone in 2023. Earlier AST SpaceMobile satellites have drawn concern from segments of the amateur radio community due to their use of frequencies in the 430–440 MHz band for telemetry and control. The company has said it is coordinating with regulators as it expands its constellation. (ANS thanks Gizmodo for the above information)
+ Tory Bruno, longtime CEO of United Launch Alliance (ULA), is joining Blue Origin as president of its newly created National Security Group. Bruno led ULA for 11 years following a 30-year career at Lockheed Martin and previously partnered with Blue Origin on development of the BE-4 rocket engine used by both companies. Blue Origin said Bruno will report to CEO Dave Limp and will focus on expanding the company’s national security launch capabilities. The move comes as Blue Origin seeks to increase its role in U.S. government launch programs while competing more directly with SpaceX. Blue Origin was added to the list of approved U.S. national security launch providers in 2024 alongside ULA and SpaceX, though its New Glenn rocket has flown only a limited number of times to date. ULA announced that John Elbon, previously the company’s chief operating officer, will serve as interim CEO. (ANS thanks GeekWire for the above information)
+ UK-based company Space Forge has successfully generated plasma aboard its ForgeStar-1 satellite, marking a milestone in commercial in-space manufacturing. The demonstration establishes ForgeStar-1 as the first free-flying commercial spacecraft to operate as a semiconductor manufacturing platform in low Earth orbit. Space Forge says the plasma test confirms that the extreme conditions required for gas-phase crystal growth can be created and controlled on an autonomous satellite. The work builds on earlier research conducted aboard the International Space Station and is aimed at producing advanced semiconductor materials in microgravity. Space Forge is focusing on wide- and ultrawide-bandgap materials such as gallium nitride and silicon carbide, which are used in power electronics and advanced communications systems. The company says microgravity conditions may enable cleaner crystal growth than is possible on Earth. Data from the ForgeStar-1 mission will be used to inform future in-space manufacturing missions. The satellite is expected to complete its mission with a controlled atmospheric reentry as part of a planned end-of-life demonstration. (ANS thanks Semiconductor Today for the above information)
Join AMSAT today at https://launch.amsat.org/
In addition to regular membership, AMSAT offers membership to:
- Societies (a recognized group, clubs or organization).
- Students enrolled in at least half-time status are eligible for free membership to age 25.
- Memberships are available for annual and lifetime terms.
Contact info [at] amsat.org for additional membership information.
73 and remember to help Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
This week’s ANS Editor,
Mitch Ahrenstorff, ADØHJ
mahrenstorff [at] amsat.org
ANS is a service of AMSAT, the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation, 712 H Street NE, Suite 1653, Washington, DC 20002
AMSAT is a registered trademark of the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation.
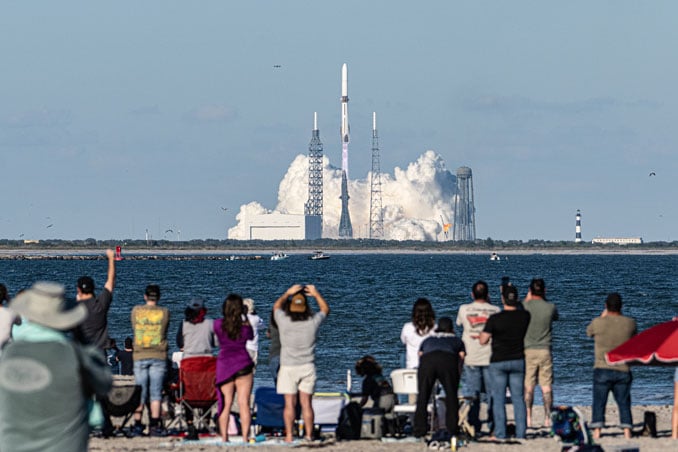






























 New Glenn lifts off from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral, carrying twin Mars probes for NASA. Image: Michael Cain/Spaceflight Now.
New Glenn lifts off from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral, carrying twin Mars probes for NASA. Image: Michael Cain/Spaceflight Now.
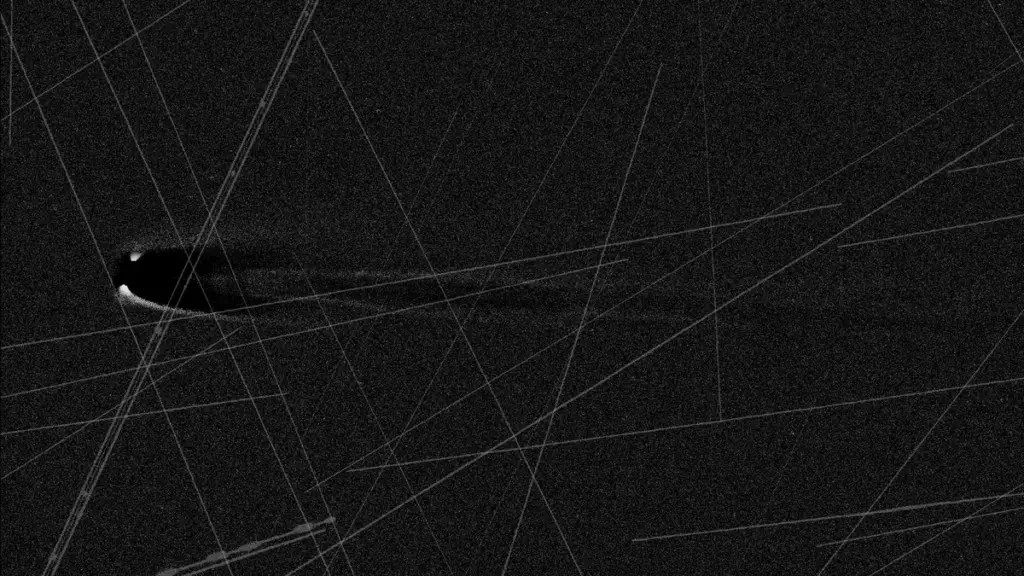 A composite image of Comet Lemmon revealing where bright pixels were rejected by an image-stacking algorithm. (Image credit: Dan Bartlett via Space.com)
A composite image of Comet Lemmon revealing where bright pixels were rejected by an image-stacking algorithm. (Image credit: Dan Bartlett via Space.com)